LISA Pathfinder releases successfully test masses which are already in free fall inside the spacecraft
Freely_Floating_in_space_large
The researcher of the Institute of Space Sciences (IEEC-CSIC) Lluís Gesa has participated in the operation that has been carried out from the European Space Operations Center (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany, and he has highlighted the importance of the release: “It is the first time that we placed two masses in freefall in the space on an experimental basis”. According to the researcher from the LISA gravitational astronomy group “this was far more critical of the mission since this mechanical and engineering action could not be tested at 100% in Earth because we cannot eliminate the gravitational field”.
It will be another week before the cubes are left completely at the mercy of gravity, with no other forces acting on them. Before that, the masses are controlled inside to follow the spacecraft movement in its flight through space. The next step is to relax this control and make the spacecraft follow the masses in a real free fall.
Once successfully passed the most crucial point of the mission, on March 1st, researchers will begin science mission.
The search for gravitational waves in space
Gravitational waves are minute fluctuations in the fabric of spacetime, predicted by Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity and directly observed for the first time recently by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory – an announcement that created a worldwide sensation last week.
As this discovery confirmed, ground-based experiments can detect high-frequency gravitational waves from cosmic events such as the coalescence of a pair of stellar remnants, like neutron stars or black holes. However, to observe lower-frequency gravitational waves emitted by different astronomical sources, such as the merging of supermassive black holes at the centre of large galaxies, it is necessary to move the search into space.
There, a future gravitational wave observatory, already identified as the goal for the L3 mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision programme, will measure distortions in the fabric of spacetime on the inconceivably tiny scale of a few millionths of a millionth of a metre over a distance of a million kilometres.
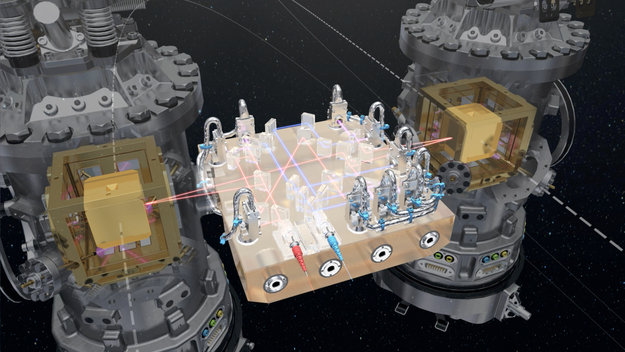
In the coming months, LISA Pathfinder will verify the fundamental condition needed for such a future gravitational wave observatory: putting test masses into freefall at unprecedented levels of accuracy, by isolating the two cubes from all external and internal forces except one: gravity.
